Submit feedback
Pneumatic Air Winch: The New Power Source for Industrial Lifting
 2025.08.01
2025.08.01
 Industry News
Industry News
With the ongoing trend of heavy industrial equipment upgrades, the performance, safety, and adaptability of lifting equipment have become key concerns for companies. As an efficient, safe, and adaptable lifting solution for complex environments, the Pneumatic Air Winch is playing an increasingly important role in numerous industrial sectors. Whether in mining operations characterized by high dust and flammable and explosive environments, or in manufacturing plants requiring precise control and long-term continuous operation, pneumatic winches, with their unique technical advantages, are an ideal power source.
Principles and Technical Foundations of Pneumatic Winch
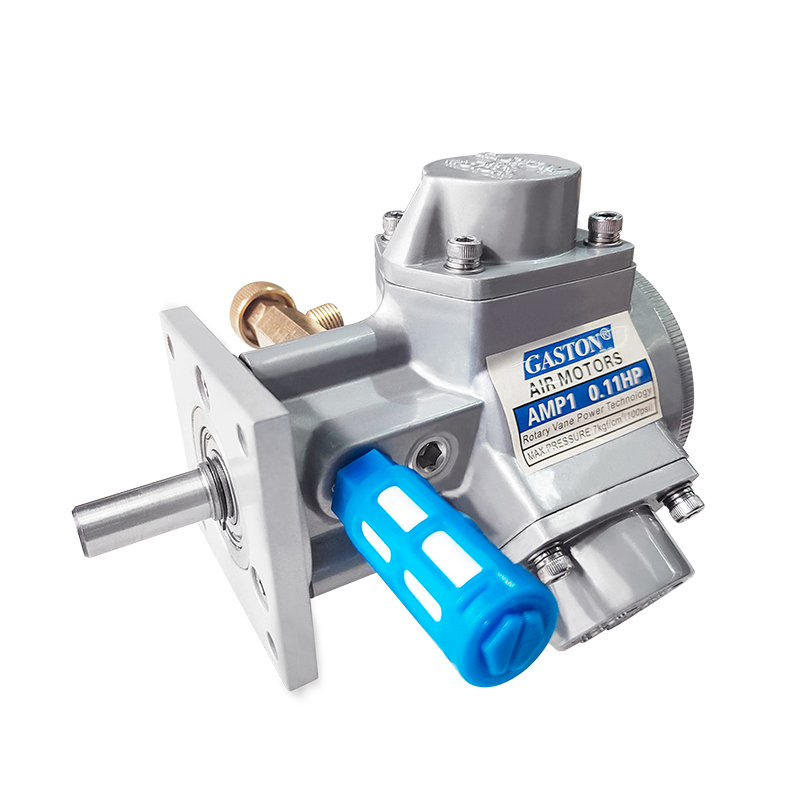
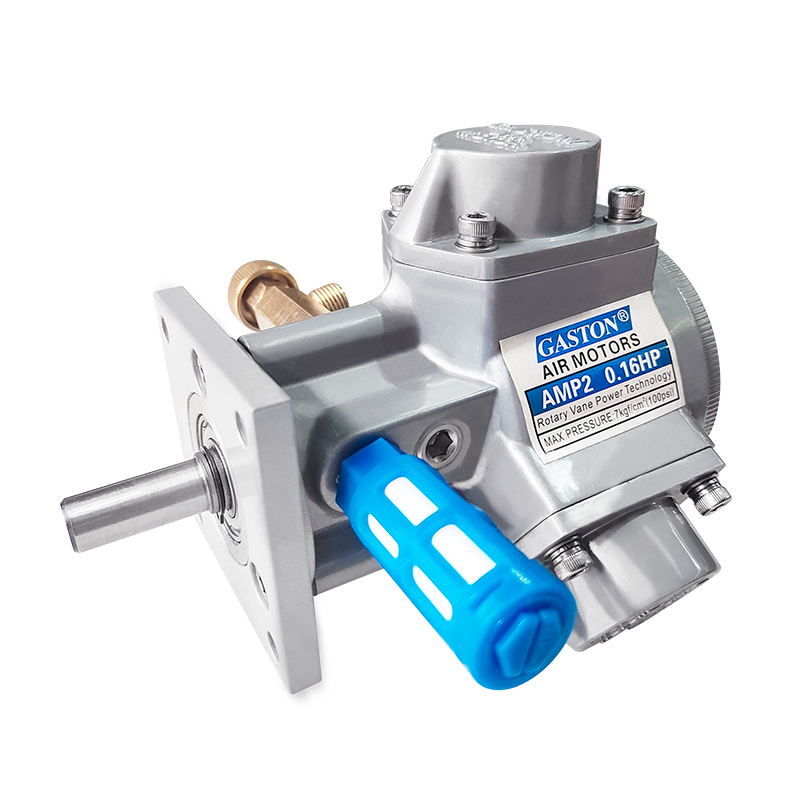
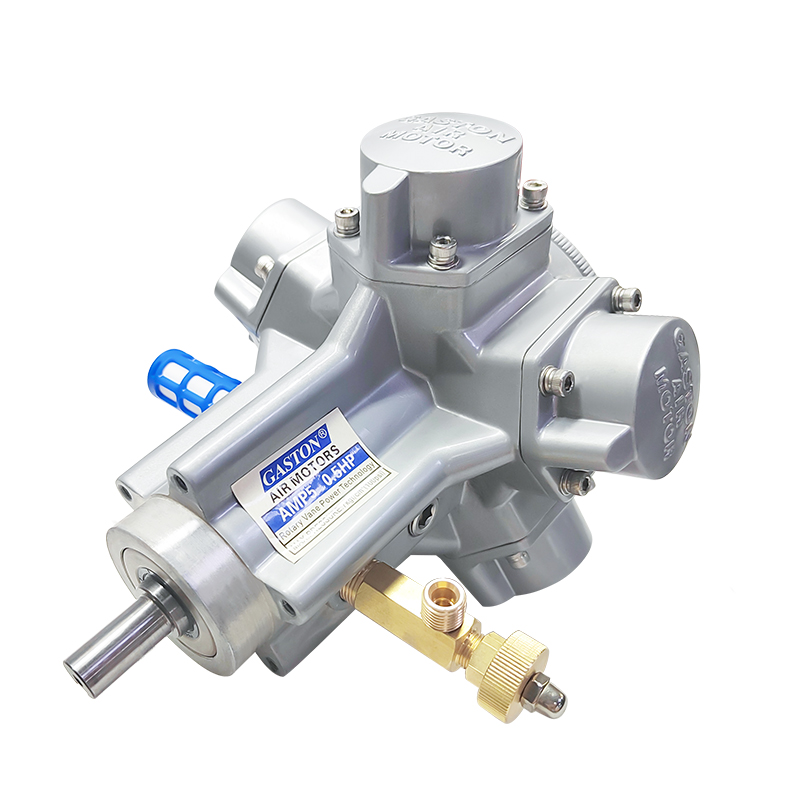
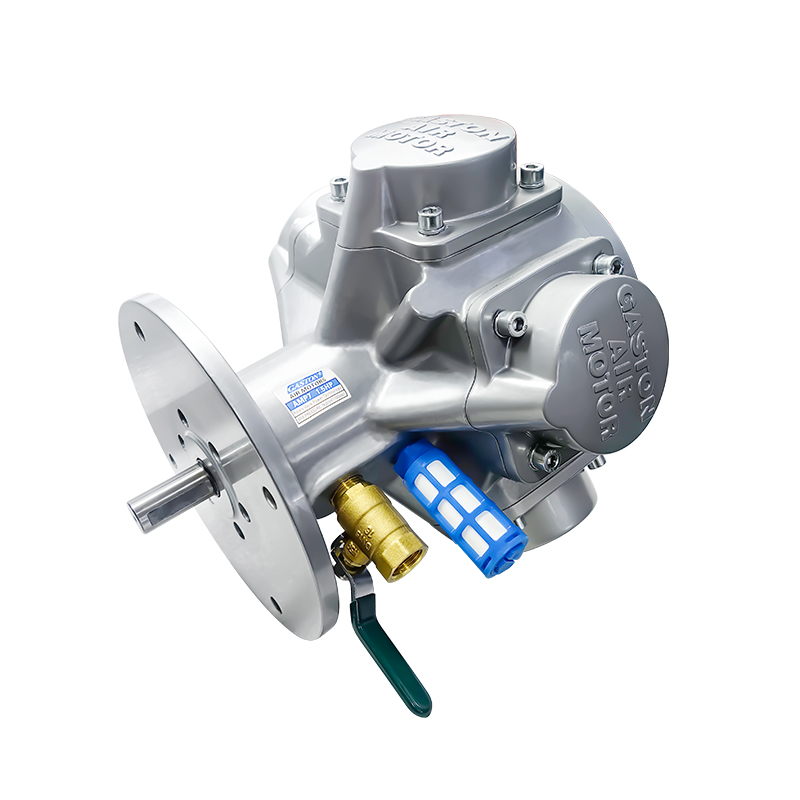
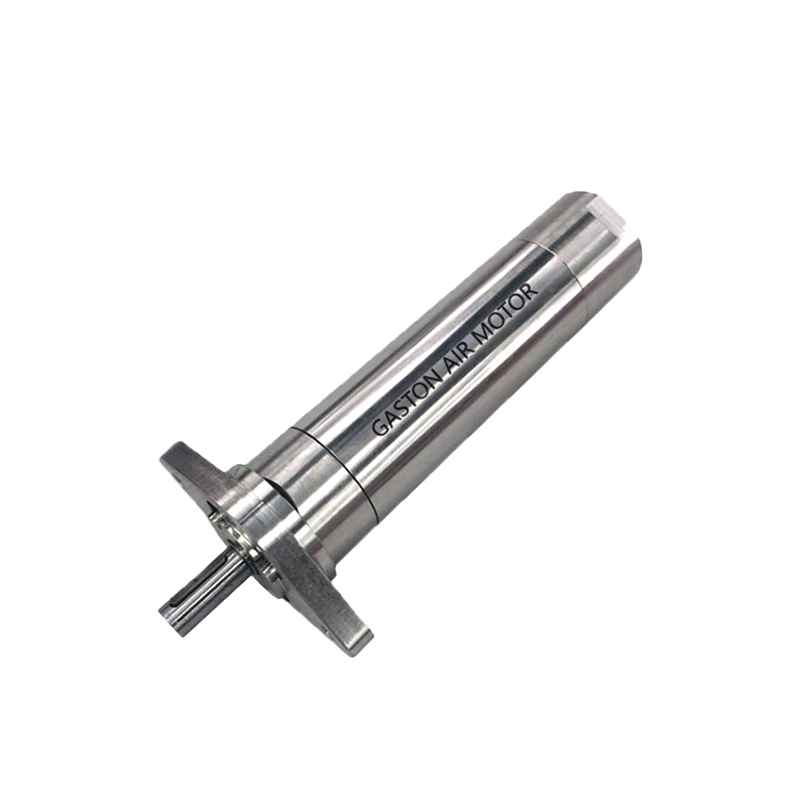
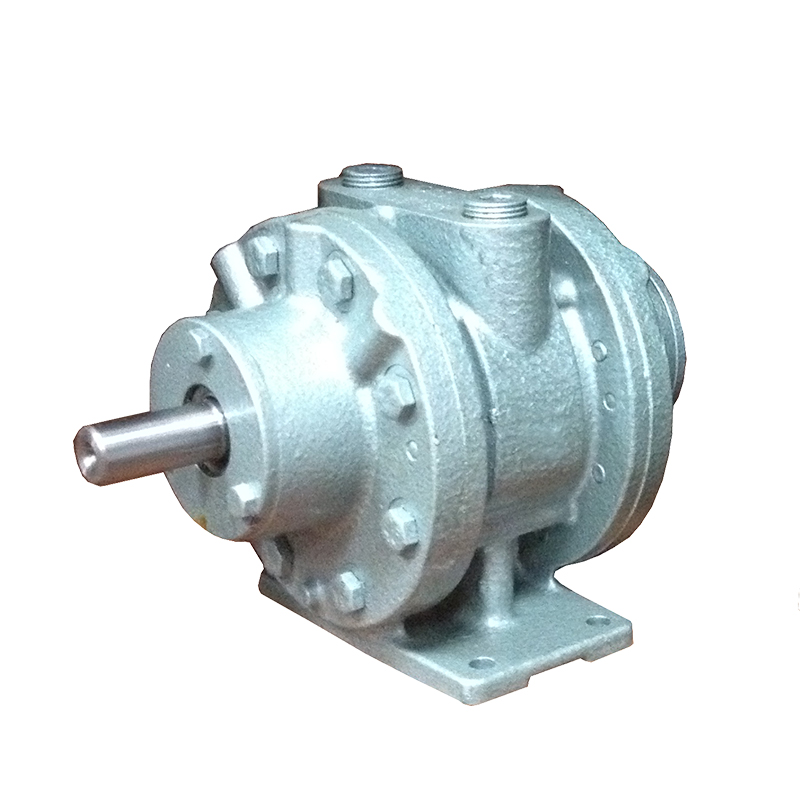
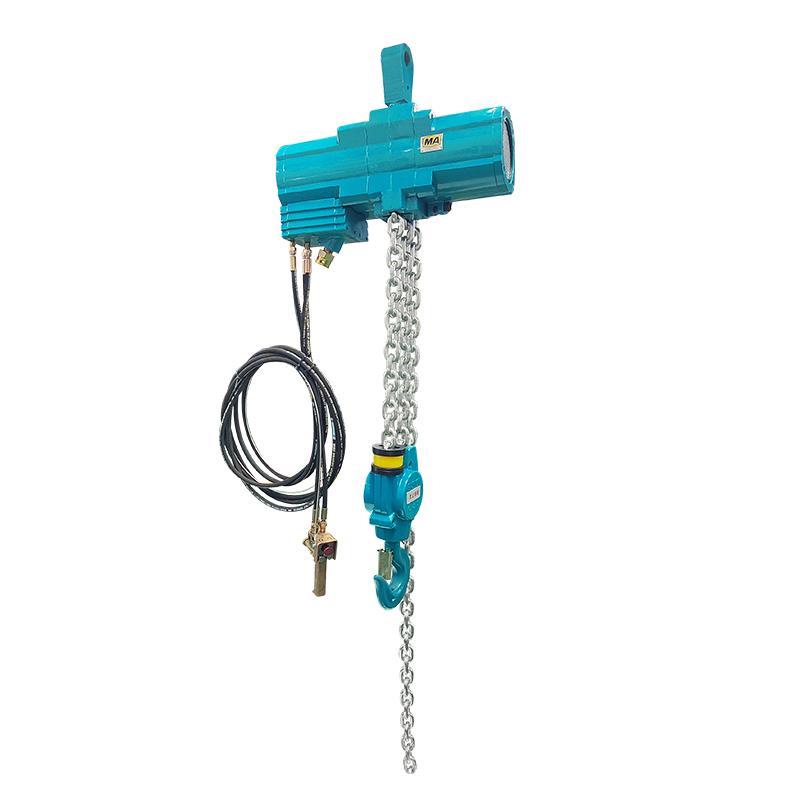
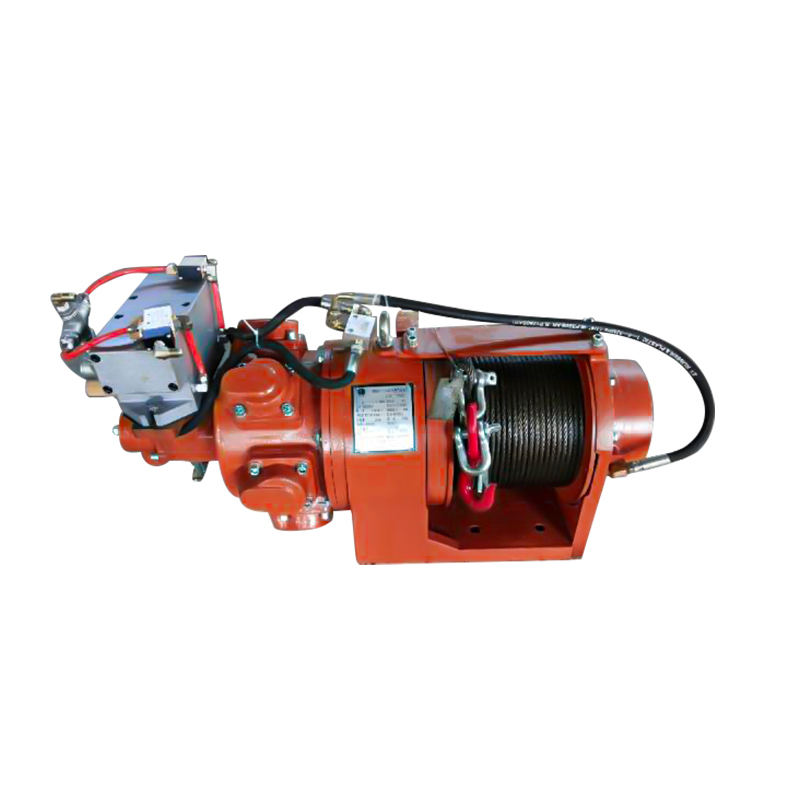
A pneumatic winch is a type of lifting equipment powered by compressed air. A pneumatic motor drives a drum to retract and release a wire rope, thereby pulling or lifting heavy objects. Compared to traditional electric or hydraulic systems, pneumatic systems are inherently explosion-proof, making them more widely used in high-risk industries such as the petrochemical industry, coal mining, and shipbuilding.
The pneumatic motor, its core drive unit, not only offers excellent torque output but also operates stably in high-temperature, high-humidity, and high-dust environments. The pneumatic system's fast response and sensitive speed regulation enable precise control of winch hoisting speed and torque, providing greater operational flexibility in complex working conditions.

Multi-Scenario Adaptability: Comprehensive Coverage from Mines to Factories
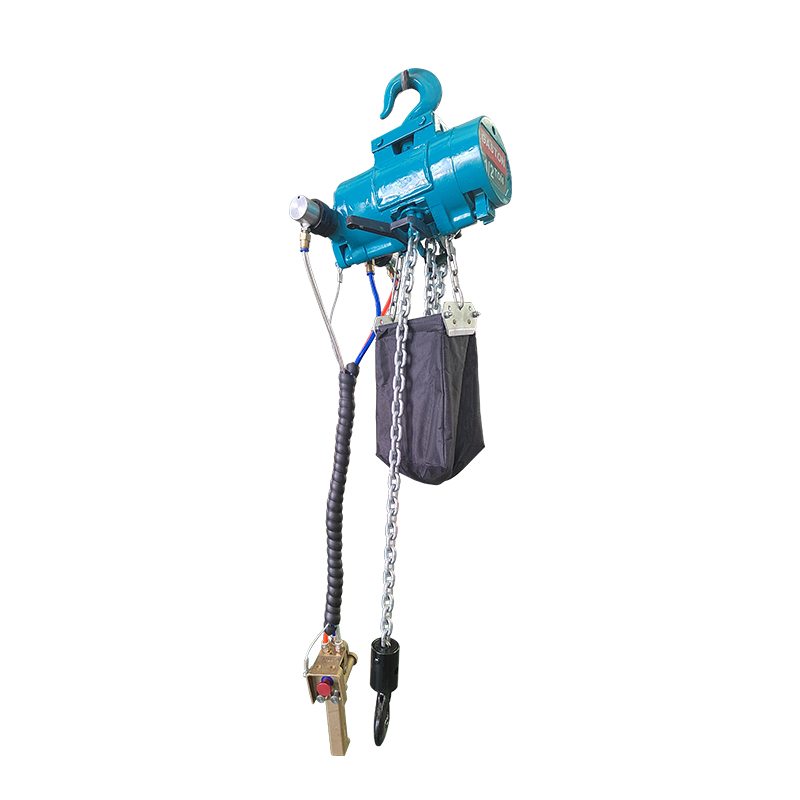
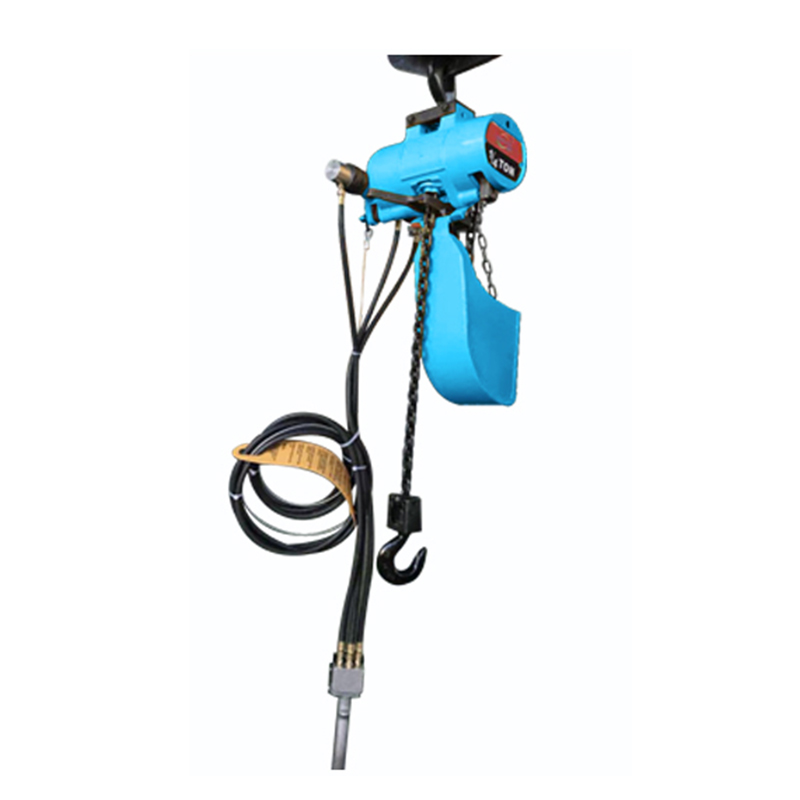
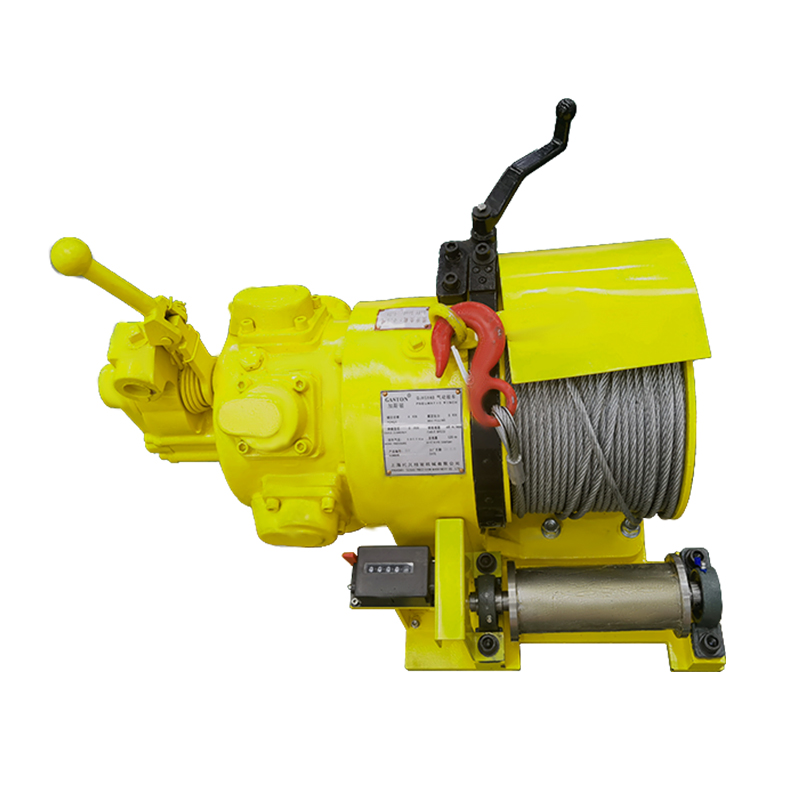
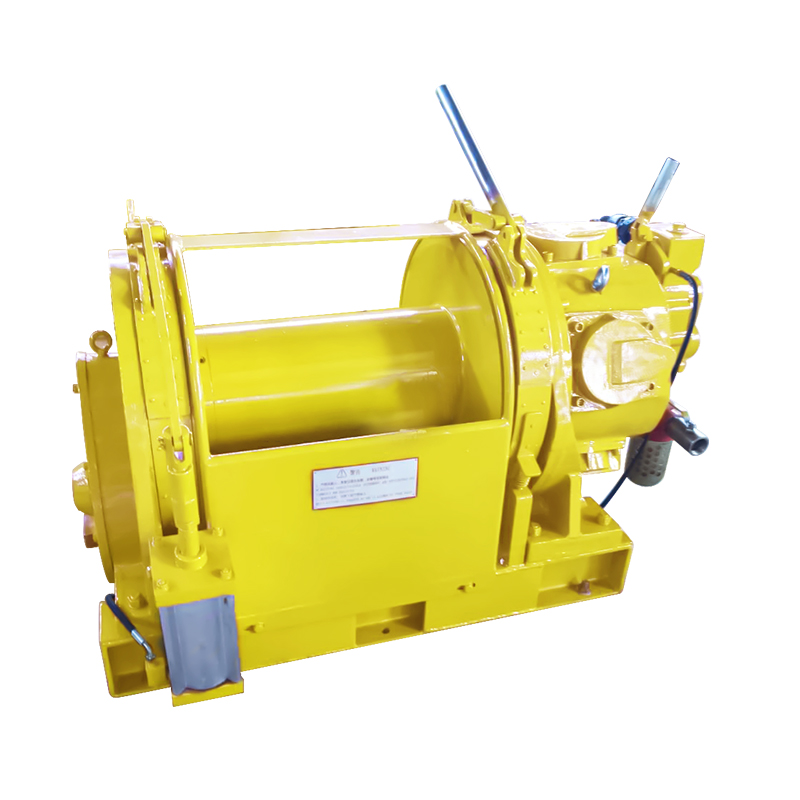
The Pneumatic Air Winch was designed with the complexities of industrial sites in mind. Its compact structure and relatively light weight make it more flexible during installation and transport, making it particularly suitable for operations where space is limited or frequent movement is required. A variety of winch models are available to accommodate loads ranging from hundreds of kilograms to several tons, meeting the demands of varying working conditions.
In mines, pneumatic winches are used for critical tasks such as personnel rescue and ore transportation, ensuring operational safety through their stability and efficiency. In factories and shipyards, they can be used in conjunction with hoisting rails or pulley systems to transport and install precision parts, improving work efficiency. In construction, winches are widely used as temporary lifting equipment due to their power-free operation and ease of operation.
Modular Design Enhances Scalability
Modern pneumatic winches mostly utilize a modular design, allowing different functional modules to be combined as needed, supporting the flexible integration of a variety of accessories. For example, limit switches, load display instruments, or remote control systems can be added to meet operating conditions, enabling remote operation and load monitoring, enhancing the intelligence of operations.
Environmental and Economic Advantages of Pneumatic Systems
Against the backdrop of global industrial energy conservation and emission reduction efforts, the environmental benefits of pneumatic systems are gaining increasing attention. Compared to electric systems, pneumatic winches generate no electromagnetic interference and require no complex electronic control circuitry, offering significant advantages in maintenance and energy management. A stable compressed air supply is all that's needed to power the entire system, reducing reliance on external energy sources.

Furthermore, pneumatic winches offer low maintenance costs and a long component replacement cycle, making them particularly suitable for long-term, high-intensity industrial applications. Their simple power transmission process and low failure rate further reduce operational risks and downtime, effectively improving overall operational efficiency.
The Pneumatic Air Winch represents more than just a technological product; it represents a new interpretation of industrial efficiency, safety, and sustainability. From technical principles to engineering applications, from structural optimization to intelligent evolution, it is gradually becoming an important force in modern industrial production lines by virtue of its stability, flexibility and high adaptability.


 English
English русский
русский Français
Français Español
Español 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى













